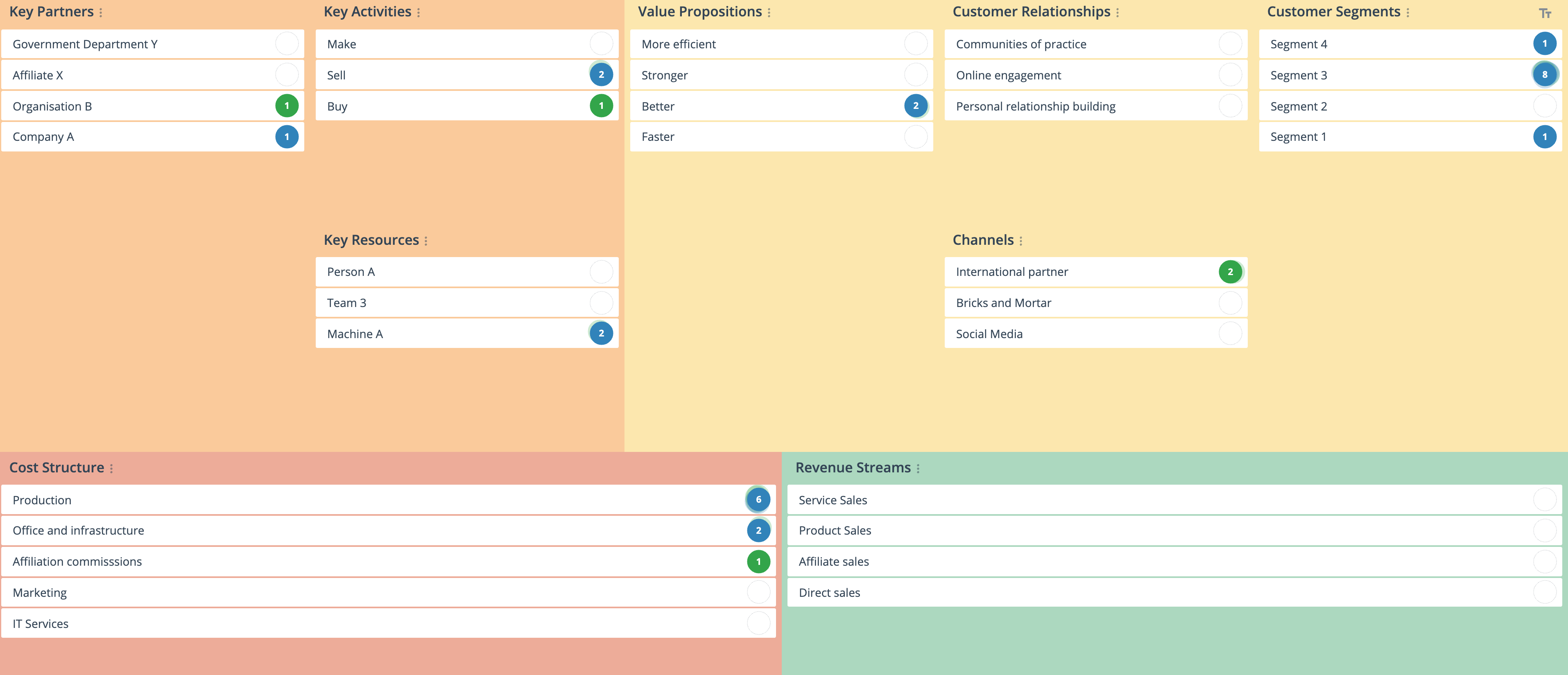
What is Business Model Canvas?
The Business Model Canvas is a visual chart documenting key aspects of a new or existing business. Designed by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur, it provides an organizational blueprint for further planning and action. The canvas collects information under nine areas critical to an organization or product’s success – addressing value proposition, customers, infrastructure, and finances.
The resulting canvas is a single-page business plan that represents how an organization creates and delivers value to its customers – or how it could do in future.
Why use the Business Model Canvas?
- Develop a holistic view of the core elements that drive the business
- Streamline planning
- Align objectives, structures, and processes
- Facilitate conversations about an organization’s strategy
- Create consistency of planning terminology across the entire organization
- Enable better collaboration across departments and sites through a shared understanding of how the business operates
- Provide a foundation for execution of strategy, prioritization of resources, and effective action planning
A Business Model Canvas requires much less documentation than a traditional business plan. Because all the information is on a single page, updates and modifications are far easier to make. The simplified layout provides a clear picture of the organization for new employees, business partners, and potential investors.
Related Templates
- Lean Canvas
- Strategy Sketch
- Petri’s FTE Canvas
- Value Proposition Canvas
- Persona Template
Tips in Using Business Model Canvas Effectively
- Carefully select participants to provide expert knowledge but also a fresh perspective.
- Use technology to involve critical people in different locations rather than miss their contribution.
- Minimize groupthink by brainstorming ideas individually then combining issues to get the overall picture.
- Be specific rather than broad when defining ideas.
- Use quantitative data where possible to focus on the crux of the issue.
- Provide adequate time in the session to rank and prioritize ideas.
- Communicate outcomes to stakeholders and regularly update progress on actions.
References
- Wikipedia
- Alexander Cowan
- Osterwalder, Alexander, and Yves Pigneur. Business model generation: A handbook for visionaries, game changers, and challengers. John Wiley & Sons, 2010
Who Should Use the Business Model Canvas?
Because the technique simplifies the business planning process, the Business Model Canvas is useful for:
- Startups and entrepreneurs
- New products or services within an existing business model
- Organizations reassessing their old business model
- Alignment of plans throughout all levels of the organization
- Organizations seeking new relationships with customers, key partners, and investors
- Consultants and advisors tasked with assisting or evaluating an organization
- Businesses undertaking mergers or acquisitions
Business Model Canvas Template
A Business Model Canvas template is structured as nine building blocks supporting four key elements of the organization: Value Proposition, Customers, Infrastructure, and Finances
The nine building blocks consist of Value Proposition, Customer Segments, Customer Relationships, Distribution Channels, Key Activities, Key Partnerships, Key Resources, Revenue Streams, and Cost Structure.
Key Partners
Partnerships, suppliers, and joint ventures fit into this segment. Partnerships leverage your resources to add further value.
Questions to ask:
- Who are your key partners/suppliers?
- Who will help you and why?
- What activities can be outsourced so your business can focus on core activities?
Key Activities
These are the actions that drive impact and value within the business.
The activities are core to creating value and drive revenue within the organization.
Questions to ask:
- What activities, if ceased would bring our business to a stop?
- What activities can be treated as value-adding, vs non-value adding?
- What do we do that is core to providing our product or service?
Key Resources
They include strategic assets you need to launch, maintain, and improve your business, product or service. For example key talent, intellectual property, physical and financial assets.
Questions to ask:
- What assets give your business a competitive edge?
- What key resources do you require to provide your value proposition?
- What resources are most important for effective distribution channels, customer relationships, and developing revenue streams?
- What infrastructure, people or funds do we have access to in support our partners or our customers?
Value Proposition
The products and services you offer, the value they provide to your customers, and reasons why they are unique fit here.
Questions to ask:
- What problems do we solve for our customers?
- What customer needs do we satisfy?
- Why do customers buy from use and not our competitors?
- What is unique about what we provide?
Customer Relationships
The way in which you attract, keep and maintain your customers fit here.
Questions to ask:
- What relationships do our customers expect us to establish and maintain with them?
- How do we interact with potential customers throughout their ‘buyer’s journey’?
Channels
The ways you let your customers know about, sell, deliver, and maintain your products and services fit here.
Questions to ask:
- Which channels can we reach our customers through and what strategy should we deploy?
- How do we effectively promote, sell and deliver our value proposition?
- Which channels work best for each customer segment?
Customer Segments
Customer segments are the groups of people for whom your business creates value. You solve their problems and meet their needs. This section provides an opportunity to perform an in-depth analysis of your customer base.
Organizations may find the development of individual personas for each segment provides greater insight into their core customers.
The organizations and people you provide products and services to and contribute to your revenue streams fit here.
Questions to ask:
- Who are our most important current and potential customers?
- What do they need or want?
- How do they think and feel?
- What do they do?
Cost Structure
The costs of all the other elements in the business model canvas fit here.
Questions to ask:
- What are the major cost drivers for our business and how are they linked to revenue and delivery of our value proposition?
- Which key resources and activities are most expensive?
- Are costs fixed or variable?
- How will costs rise as we grow?
Revenue Streams
The products and services customers are willing to pay for, and how they do that fit here.
Questions to ask:
- What are your customers willing to pay for? How much are they willing pay?
- How do they prefer to pay?
- How much does each revenue stream contribute to the overall total?
How to Build an Effective Business Model Canvas
To obtain the best possible outcomes from your Business Model Canvas, look for alignment between the different areas; especially customer segments and your value proposition. Map the customer journey from the first point of contact, through purchase and then ongoing maintenance. Don’t be afraid to remove anything that doesn’t make sense.
While you can map the Business Model Canvas according to the current status quo, you should also consider how key market and industry forces, along with macroeconomic trends, will impact your future.
Brainstorm
As a team, discuss and populate each section of the canvas.

Vote
Individually vote on the areas you need to focus on.
Action Planning
Create actions for each of the top focus areas. Assign responsibility and timeframes.
Share and Communicate
Share the outcomes of the session, including the action plan, to relevant stakeholders.
Gather ideas individually or as a group using a whiteboard, post-it notes, or an online tool like GroupMap. Start by identifying who your business serves – Customer Segments. Then describe what you offer and why – Value Proposition. Next, comes all the things you need to do to deliver your offering to your customers – Channels, Relationships, Activities, Resources, Partnerships. Finally, address the financial aspects of your business – Revenue and Costs.
Once you have everybody’s ideas, they need to be organized. Cull any duplicates and discard any not in scope. Then work together to prioritize the consolidated ideas in each of the nine sections of the Canvas.
If the brainstorming step was performed by individuals, rather than as a group, this may take considerably longer than if you gathered ideas as a group. Software tools like GroupMap can significantly reduce the time and effort required to group and rank ideas, and the outcome is likely to be better.
Identify actions required for each item and assign responsibility for progressing them to individuals or teams. Make sure you set clear timeframes for completion.
Distribute the resulting Business Canvas Model and action plan to all relevant stakeholders and monitor progress and effectiveness on a regular basis. GroupMap automatically generates visually appealing reports and action plans in several formats for distribution, saving time and effort after the analysis.
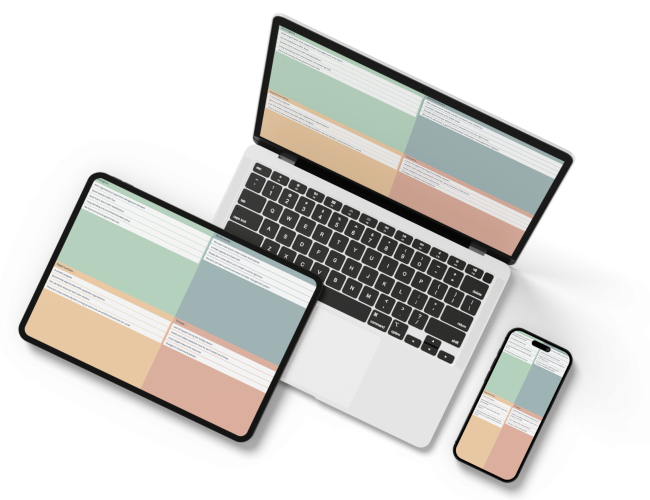

Save Effort, Time and Money with GroupMap
GroupMap offers more than just an online digital whiteboard—it’s innovative platform is designed to enhance the quality of your team’s decisions. With features that prevent bias and make facilitation seamless, GroupMap ensures no single voice dominates and ensures productive, inclusive conversations.
Its intuitive interface is easy for anyone to use, and its scalable design supports small teams and large groups whether they are face to face or around the globe. Customisable templates and workflows keep discussions focused on objectives, helping you drive actionable outcomes each and every time.
Create your first map and invite people in to start sharing their thoughts NOW.
Experience the power of GroupMap with our FREE 14 day trial.
Your free trial gives you access to all of our features, no credit card required.
