What is a Lean Canvas?
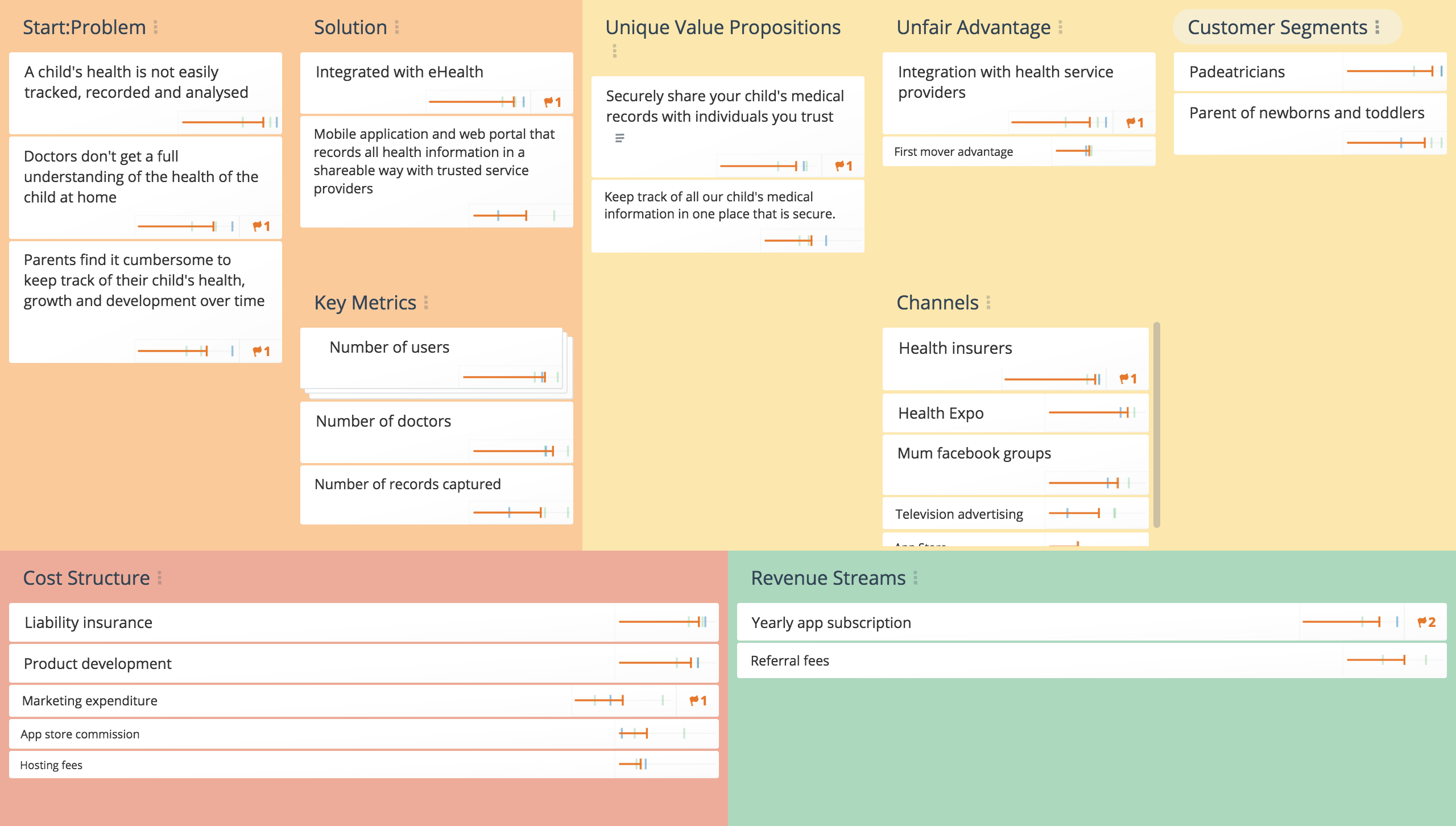
The Lean Canvas is an entrepreneur-focused planning tool that identifies the key aspects of a business in a simple actionable 1-page business plan. The Lean Canvas was adapted from the Business Model Canvas by Ash Maurya and focuses on nine areas critical specific to the Lean Startup methodology.
The nine areas are Problem, Solution, Key Metrics, Unique Value Proposition, Unfair Advantage, Customer Segments, Channels, Cost Structure, and Revenue Streams.
Central to the Lean Canvas approach is the need to understand your customer’s problems as the first step before you can focus on the solutions to those problems and how to deliver them to the market.
The resulting chart represents how an organization creates and delivers value to its customers – or how it could do so in future.
What is a Lean Canvas Used For?
Use a Lean Canvas is to evaluate the potential of an idea before allocating time, effort, and resources into development. A one-page Lean Canvas is much faster and easier to create than a multi page business plan. It’s brevity, and simple format is readily understood by stakeholders and investors and easy to update in response to changes in business conditions. Use it to:
- Develop an overview of the critical aspects that drive a business
- Streamline planning
- Facilitate conversations about an organization’s strategy
- Create an understanding of the plan across the entire organization
- Help employees collaborate better through a shared understanding of how the business operates and it’s environment.
- Underpin strategy execution, resource prioritization, and effective action plans.
The Benefits of the Lean Canvas Model.
The model is equally effective for both small and large businesses and is particularly useful for startups and entrepreneurs, and new products or services within an existing business.
As the organization or product develops, the Lean Canvas can evolve into a Business Model Canvas.
- Business Model Canvas
- Value Proposition Canvas
- Persona Template
- Strategy Sketch
- Petri’s FTE Canvas
- If your customers have multiple pain points you can list them allbut then narrow these down to the top real pain points through user tests, interviews or questionnaires.
- Explore alternatives and competitors who are in your space to see how they address aspects of your Lean Model Canvas.
- Brainstorming generic value propositions or unfair advantages is dangerous. Ask yourself what makes you really stand out. A brand perceptual map can help answer this question.
- There are hundreds of metrics to choose from so start with those that are relevant to the stage of your business and can be economically measured. Churn rates might not be as valuable as acquisition rates when you first launch your start up.
- The Lean Canvas needs to change and evolve as you learn more. Adding a second stage, or duplicating a new version lets you see how things have changed over time.
- Don't get stuck - it's important to let old assumptions die and replace them with new ones.
- Ask and be prepare for feedback. Having a lean canvas model is a great tool for mentors and advisors to review and provide insight or ask questions.
- Wikipedia
- Ash Maurya
- Example Templates
The Lean Canvas Template
Problem
Questions to ask:
- What are the top problems our potential customers face?
- What are the existing alternatives that solve those problems (competitors)?
Solution
Questions to ask:
- How do we, or can we solve the problem.
- What is the Minimum Viable Product (MVP) that will address the problems?
Key Metrics
Questions to ask:
- What is the single most important measure that drives what we do?
- How will we know we are succeeding?
Unique Value Proposition
Questions to ask:
- What is unique about what we provide?
- Why would a customer choose our solution over other alternatives?
Unfair Advantage
Questions to ask:
- What do we do or have that deters copy cats and competitors and which can’t be bought?
Channels
Questions to ask:
- How do/should we, sell, deliver, and maintain our products and services.
- Which channels work best for each of our customer segments?
- Which channels are the most cost effective?
Customer Segments
Questions to ask:
- Who are our most important current and potential customers?
- What do they need or want?
- How do they think and feel?
- What do they do?
Cost Structure
Questions to ask:
- What are the primary cost drivers for our business and how do they relate to revenue and delivery of our Unique Value Proposition?
- Are costs fixed or variable?
- How will costs scale as we grow?
Revenue Streams
Questions to ask:
- What products and services are customers willing to pay for?
- How do they prefer to pay?
- How much does each revenue stream contribute to the overall total?
Lean Canvas vs Business Model Canvas
Like the Business Model Canvas, a Lean Canvas template has nine building blocks that combine to build a holistic overview of an organization’s strategy. Unique Value Proposition, Customer Channels, Customer Segments, Cost Structure, and Revenue Streams are common to both.
However, Ash Maurya made the model more entrepreneur-focused by replacing four of the nine elements
Key Partners → Problem
Key Activities → Solution
Key Resources → Key Metrics
Customer Relationships → Unfair advantage
These changes target newer business ideas, start-ups, internal company skunk work projects and spin-offs. It means that it accounts for greater uncertainty and allows the attention to be focussed on more empathetic as well as innovative solutions through identifying key problem areas for customers.
How to Create a Lean Canvas
When developing your Lean Canvas, it’s critical to define and articulate your customer segments and their problems accurately first. After that, the rest of the canvas flows – Solutions, Unique Value Proposition, Unfair Advantage, Channels, Costs, Revenue, and Key Metrics.
It’s unlikely you will create a final plan in one session. Your canvas will develop as you test your assumptions against the realities of your market.
A key step is to “test” the feasibility of the idea. You can rate each aspect of the canvas to determine which parts represent the greatest risk and need more validation. This helps to focus the conversation, energy, and effort of the team onto aspects that are most impactful. With GroupMap, you can rate ideas to allow you to discover which risk areas need to be addressed and plan action items.
Brainstorm
Discuss and populate each section of the canvas.

Rate
Identify aspects of your business that need the most validation.
Action Plan
Create actions for the top focus areas. Assign responsibility and time frames.
Share
Share, communicate and iterate on your lean canvas to refine your business model.
Gather ideas individually or as a group using a whiteboard, post-it notes, or an online tool like GroupMap. Start by identifying who you believe you are building your product or service for – Customer Segments. Then describe what their Problem is.
Next, decide on how you can provide a Solution to that problem. You can now work through the other areas of the canvas to work out what you have or need to deliver those solutions to your customers – Unique Value Proposition, Unfair Advantage and Channels.
With all those aspects in place you should be able to address the financial aspects of your business – Revenue and Costs.
The final step is to develop your Key Metrics.
As a group or as individuals, use rating scales to indicate which aspects of your lean canvas require the highest level of validation (things you need to do remove assumptions to prove that the business idea is feasible.)
A low validation score means that it is a known fact or supported by data and represents low risk to the business model.
An high validation score means that it is currently an assumption that has to be tested, researched or represents the need to explore due to the risk it introduces to the business model.
Identify actions that will help to validate the assumption.
Examples might include interviewing 100 potential customers, running a technical test on a rapid prototype, undertaking research activities, a competition scan or through the creation of a persona empathy map.
Distribute your Lean Canvas and action plan to the team and your mentors. Use the plan to monitor progress regularly. Update the canvas as the business and product evolve. GroupMap ensures that your lean model canvas can continue to be a living, breathing document that allows you to change and expand it as your business does too.

Save Effort, Time and Money with GroupMap
GroupMap offers more than just an online digital whiteboard—it’s innovative platform is designed to enhance the quality of your team’s decisions. With features that prevent bias and make facilitation seamless, GroupMap ensures no single voice dominates and ensures productive, inclusive conversations.
Its intuitive interface is easy for anyone to use, and its scalable design supports small teams and large groups whether they are face to face or around the globe. Customisable templates and workflows keep discussions focused on objectives, helping you drive actionable outcomes each and every time.
Create your first map and invite people in to start sharing their thoughts NOW.
Experience the power of GroupMap with our FREE 14 day trial.
Your free trial gives you access to all of our features, no credit card required.
